Difference between revisions of "Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools"
m (→Introduction) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | This tutorial explains the creation of '''[[enemy routes in battle arenas]]''' using '''[[Wiimms SZS Tools]]'''. Make sure you have understood the concept of '''Standard Routes and [[Dispatch Point]]s'''! | |
| − | |||
| − | This tutorial explains the creation of '''[[enemy routes in battle arenas]]''' using '''[[Wiimms SZS Tools]]'''. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 10: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| − | As of v1.60a, [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] support an automatic connection of '''Standard Routes''' and '''[[Dispatch Point]]s'''. All you need is to | + | As of v1.60a, [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] support an automatic connection of '''Standard Routes''' and '''[[Dispatch Point]]s'''. All you need is to set up the routes and points, edit some settings to advise the KMP compiler, and run the compiler. [[Bash 'n' Dash 'n' Battle (Bash 'n' Dash 'n' Bash Edit)|Bash 'n' Dash 'n' Battle]] is the first arena that used this feature. |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
There is a second page with full ''[[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples|code examples]]'', which are used as reference from this page. | There is a second page with full ''[[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples|code examples]]'', which are used as reference from this page. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 13: | ||
[[File:Wiimms KMP Compiler.png|250px|thumb|KMP conversions by [[Wiimms SZS Tools]]]] | [[File:Wiimms KMP Compiler.png|250px|thumb|KMP conversions by [[Wiimms SZS Tools]]]] | ||
| − | + | When a tool of [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] reads a file, the process is always the same: the file is read into memory and analyzed to find out the file format. If the file has an acceptable file format, a scan function is selected and the file data is scanned and translated into the internal data structures, which can hold more data than the files. | |
| − | In case of [[KMP]] (see image on the right), ''native KMP files'' and ''text KMP files'' are accepted for input. For SZS archives, file '''course.kmp''' is searched and scanned. Native are scanned by a binary scanner and text files by | + | In case of [[KMP]] (see image on the right), ''native KMP files'' and ''text KMP files'' are accepted for input. For SZS archives, the file '''course.kmp''' is searched for and scanned. Native files are scanned by a binary scanner and text files are translated by the KMP compiler. |
| − | [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] use a 2-pass compiler to translate KMP text files into the internal data structure. On each pass the complete text file is scanned. In the first pass the file is scanned for name definitions. This allows | + | [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] use a 2-pass compiler to translate KMP text files into the internal data structure. On each pass, the complete text file is scanned. In the first pass, the file is scanned for name definitions. This allows the use of name before it is defined (forward references). Error messages are suppressed. The second pass is used to set up the internal data structure. Error messages about syntax errors or missing names are printed. |
'''The concept of the 2-pass compiler is important for this article, because route links are created by names that are defined later!''' | '''The concept of the 2-pass compiler is important for this article, because route links are created by names that are defined later!''' | ||
| − | The internal data structure allows manipulations of the data | + | The internal data structure allows manipulations of the data in different ways independent of the external file format. Manipulations are for example transformations, but also automatic route connections. |
| − | At the end, the data is is stored | + | At the end, the data is is stored as binary (commands ENCODE, PATCH), as text (commands DECODE, PATCH, CAT), or dropped (command CHECK). |
| − | |||
== Standard routes only == | == Standard routes only == | ||
[[File:ENPT of Luigi Circuit.png|250px|thumb|ENPT routes of Luigi Circuit]] | [[File:ENPT of Luigi Circuit.png|250px|thumb|ENPT routes of Luigi Circuit]] | ||
| − | All 32 original racing tracks, and all custom tracks too, | + | All 32 original racing tracks, and all custom tracks too, use standard routes. In this case, each end of the routes is linked from 1 to 6 beginnings of other routes. The NEXT links are used for these connections. To get bidirectional links, the PREV links of the destinations are set to the previous routes. The PREV links can be set automatically by analyzing all NEXT links. Wiimm's tools does it, if parameter '''@AUTO-CONNECT''' is set to '''AC$PREV'''. |
| − | Let's look the group headers of '''Luigi Circuit'''. You can find the full de-compiled enemy route definition [[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples#t11|here]]. | + | Let's look at the group headers of '''Luigi Circuit'''. You can find the full de-compiled enemy route definition [[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples#t11|here]]. |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
@AUTO-CONNECT = AC$PREV # == automatic calculation of PREV links | @AUTO-CONNECT = AC$PREV # == automatic calculation of PREV links | ||
| Line 50: | Line 43: | ||
$GROUP G2B, next: G3A G3B | $GROUP G2B, next: G3A G3B | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | Lines beginning with »#« are comments. Here they show the numerical route index and the links in | + | Lines beginning with »#« are comments. Here they show the numerical route index and the links in both directions. For Wiimm's tools, the »$GROUP« tells the compiler to start a new group. The group names are generic, as well as the numbering of group names following the links. In this example, group G1 has 2 successors named G2A and G2B. The PREV links are not defined, because they are calculated automatically. |
This concept works for battle arenas too. Nintendo used it for '''SNES Battle Course 4 (A21)'''. Anyway, using dispatch points is the better concept for battle arenas. | This concept works for battle arenas too. Nintendo used it for '''SNES Battle Course 4 (A21)'''. Anyway, using dispatch points is the better concept for battle arenas. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 50: | ||
[[File:ENPT of GCN Cookie Land.png|250px|thumb|ENPT routes of GCN Cookie Land]] | [[File:ENPT of GCN Cookie Land.png|250px|thumb|ENPT routes of GCN Cookie Land]] | ||
| − | 9 of 10 battle arenas by Nintendo use [[Dispatch Point]]s. Here we use '''GCN Cookie Land''' as example. You can find the full | + | 9 of 10 battle arenas made by Nintendo use [[Dispatch Point]]s. Here we use '''GCN Cookie Land''' as an example. You can find the full decompiled enemy route definition [[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples#a24|here]]. |
| − | The text creator of Wiimm's tools | + | The text creator of Wiimm's tools prints the standard routes like this: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 | # zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 | ||
| Line 66: | Line 59: | ||
.... some points | .... some points | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | Each group name begins with »G« like usual. The group name is followed by the NEXT list. This is the same as for racing tracks. In a second line the PREV links are listed. It is needed because the links are individual and not based on the NEXT links. | + | Each group name begins with »G« like usual. The group name is followed by the NEXT list. This is the same as for racing tracks. In a second line, the PREV links are listed. It is needed because the links are individual and not based on the NEXT links. |
| − | A [[Dispatch Point]] looks similar, but the names begin »DP«. This makes differentiation between both route types easier: | + | A [[Dispatch Point]] looks similar, but the names begin with »DP«. This makes differentiation between both route types easier: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# zero based index: 10, prev:, next: 0 3 7 | # zero based index: 10, prev:, next: 0 3 7 | ||
| Line 76: | Line 69: | ||
.... exact one point | .... exact one point | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | The PREV list is empty. | + | The PREV list is empty. Since there are route setting with values other than zero, an additional $SETTINGS line is printed. |
== How to create a good ENPT setup == | == How to create a good ENPT setup == | ||
| + | Everything explained above is a large introduction, and here begins the real tutorial with the basics. A later chapter »[[#tune|Fine Tuning]]« will show, how to handle special cases like route to route links, routes on 2 or more levels and one-way links (e.g. for jumping down). | ||
| − | + | The base tutorial consists of 4 parts: | |
| − | + | * Creating a KMP text file from a binary KMP or from a SZS. | |
| − | The base tutorial consists of | + | * Editing the text file. |
| − | * | + | * Verifying the edits. |
| − | * Editing | + | * Creating the updated KMP or SZS. |
| − | * Creating the | ||
=== Creating a KMP text file === | === Creating a KMP text file === | ||
| + | [[Wiimms SZS Tools]] are not good to insert routes. There are graphical tools that are definitely better, but this is not really a problem. Insert your routes and your dispatch points too. There is no need to link them, the KMP compiler will do it for you and more. | ||
| − | + | If you have a binary KMP, just do one of the following: | |
| − | |||
| − | If you have a binary KMP, just do one of: | ||
wkmpt decode course.kmp --battle -od course.kmp.txt | wkmpt decode course.kmp --battle -od course.kmp.txt | ||
wkmpt cat course.kmp --battle >course.kmp.txt | wkmpt cat course.kmp --battle >course.kmp.txt | ||
| − | Both commands do the same: | + | Both commands do the same: load the binary KMP and write a text KMP. |
If you KMP is part of a SZS file, you can use the same commands: | If you KMP is part of a SZS file, you can use the same commands: | ||
| Line 100: | Line 92: | ||
wkmpt cat ARENA.szs --battle >course.kmp.txt | wkmpt cat ARENA.szs --battle >course.kmp.txt | ||
| − | It is also possible to extract the whole KMP and re-create the SZS later with the | + | It is also possible to extract the whole KMP and re-create the SZS later with the updated KMP: |
wszst extract ARENA.szs --battle | wszst extract ARENA.szs --battle | ||
In this case, a directory named ARENA.d is created. | In this case, a directory named ARENA.d is created. | ||
'''Some notes about options:''' | '''Some notes about options:''' | ||
| − | * Option --battle | + | * Option --battle disables the auto detection of battle arenas and tells the tools that the track file is definitely a battle arena. |
* The tools usually don't overwrite existing files. Option '''--overwrite''' or short '''-o''' disables this security mode. | * The tools usually don't overwrite existing files. Option '''--overwrite''' or short '''-o''' disables this security mode. | ||
* Option '''--dest FILE''' or '''-d FILE''' selects another destination (output) file. | * Option '''--dest FILE''' or '''-d FILE''' selects another destination (output) file. | ||
| − | * '''-od FILE''' is | + | * '''-od FILE''' is a short form of '''-o -d FILE''', which is a short form of '''--overwrite --dest FILE'''. |
| − | * '''>FILE''' | + | * '''>FILE''' redirects the output to FILE. |
If you are unsure about using the command line, then read [https://szs.wiimm.de/info/command-line.html this]. Windows users can also create batch files like: | If you are unsure about using the command line, then read [https://szs.wiimm.de/info/command-line.html this]. Windows users can also create batch files like: | ||
| Line 119: | Line 111: | ||
=== Edit the ENPT section === | === Edit the ENPT section === | ||
| − | |||
The next part is a loop of editing the text file and verifying the results. | The next part is a loop of editing the text file and verifying the results. | ||
| − | To edit the text KMP you need a text editor, but not a document editor like '''Microsoft Word'''. A recommendation for Windows users is [https://notepad-plus-plus.org/ | + | To edit the text KMP you need a text editor, but not a document editor like '''Microsoft Word'''. A recommendation for Windows users is [https://notepad-plus-plus.org/ Notepad++]. |
| − | Open the KMP text file with the editor. In | + | Open the KMP text file with the editor. In all the cases above, the filename is '''course.kmp.txt'''. |
| − | + | Then, scroll to the '''[ENPT]''' section. Don't remove or edit any other part, if you don't know what you do. They are needed to re-create the complete KMP file. | |
Make the following setting (edit the line): | Make the following setting (edit the line): | ||
@AUTO-CONNECT = AC$DISPATCH | @AUTO-CONNECT = AC$DISPATCH | ||
| − | Below the marker '''#ENPT#''' (a comment) you find the | + | Below the marker '''#ENPT#''' (a comment) you will find the decoded routes. In case of ''GCN Cookie Land'', it looks like [[Creating enemy routes of battle arenas with Wiimm's tools/code examples#a24|here]] listed. |
| − | First, we edit the standard routes. Change this ... | + | First, we edit the standard routes. Change this... |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 | # zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 | ||
| Line 140: | Line 131: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$GROUP G1 | $GROUP G1 | ||
| − | </pre>... for all standard routes to remove the manual links. | + | </pre>...for all standard routes to remove the manual links. |
| − | Dispatch points | + | Dispatch points look different. Change this... |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# zero based index: 9, prev:, next: 1 3 4 | # zero based index: 9, prev:, next: 1 3 4 | ||
| Line 151: | Line 142: | ||
<pre> $GROUP DP1 | <pre> $GROUP DP1 | ||
$SETTINGS: 1 0x40 | $SETTINGS: 1 0x40 | ||
| − | </pre>and remove the PREV and NEXT links. Keep the $SETTINGS line, if you want to keep the settings. | + | </pre>...and remove the PREV and NEXT links. Keep the $SETTINGS line, if you want to keep the settings. |
| − | If you | + | If you have removed all links, you can run the KMP compiler to verify your settings (see next section). The auto-connect function works like this: |
| − | # First all routes are divided into 2 sets: | + | # First all routes are divided into 2 sets: standard routes and dispatch points. This is done automatically, but can be controlled by [[#dpmode|special settings]]. |
| − | # Then the PREV and NEXT list of all standard routes are analyzed. If an empty list is found, the nearest dispatch point of same class is searched and linked. The [[#class|class concept]] is explained in the [[#tune|Fine Tuning]] part of this tutorial ⇒ ignore it for | + | # Then, the PREV and NEXT list of all standard routes are analyzed. If an empty list is found, the nearest dispatch point of same class is searched and linked. The [[#class|class concept]] is explained in the [[#tune|Fine Tuning]] part of this tutorial ⇒ ignore it for now. |
| − | # Now, all dispatch | + | # Now, all dispatch points are analyzed. If the NEXT list is empty, then all standard routes pointing to the dispatch point are searched. For up to 6 routes, a NEXT link is inserted. |
=== Verify your edits === | === Verify your edits === | ||
| + | There are 2 good ways to verify your edits: | ||
| + | * Create a new text KMP from the edited KMP and verify it with an editor, or with the console. | ||
| + | * Create an [[OBJ]] file and load it with your favorite [[3D Tool]]. | ||
| + | After verification, you can edit the text KMP again for a next loop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Create a new text KMP ==== | ||
| + | You can use the same commands described above to create a new text KMP with the edited text as source: | ||
| + | wkmpt decode course.kmp.txt -od verify.txt | ||
| + | wkmpt cat course.kmp.txt >verify.txt | ||
| + | |||
| + | If working with a console window, it is possible to pipe the output to a pager and scroll through it. The following command works for Windows and Linux: | ||
| + | wkmpt cat -N course.kmp.txt | more | ||
| + | |||
| + | Linux users (Cygwin users too) can use the more powerful tool '''less''' instead of the classic '''more''': | ||
| + | wkmpt cat course.kmp.txt |& less +/'^!|#ENP' | ||
| + | The option '''+/'^!|#ENP' ''' enables searching for errors and data of sections ENPH and ENPT. Type »n« to jump to the next matching line. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Section ENPH gives an overview about all routes and its links. Section ENPT shows the routes with the new calculated connections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Create an OBJ file ==== | ||
| + | A second method for verification is to export the data to a Wavefront [[OBJ]] file and to open it with any [[3D Tool]]. | ||
| + | wkmpt draw course.kmp.txt --draw enpt,white -od path/to/a.obj | ||
| + | With these options, only the enemy routes are drawn. A white ground is added for an optimal view from the top. The example image from above is made by this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alternatively, you can visualize the [[KCL]]: | ||
| + | wkmpt draw course.kmp.txt --draw enpt,kcl -od path/to/a.obj | ||
=== Create a new course.kmp or TRACK.szs === | === Create a new course.kmp or TRACK.szs === | ||
| − | + | To create a binary KMP, use the command: | |
| + | wkmpt encode course.kmp.txt -od new-course.kmp | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you have extracted a complete SZS file, use the following command to create a new one: | ||
| + | wszst create ARENA.d -od new.szs | ||
| + | If you modify the file course.kmp.txt, a new course.kmp is automatically created. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span id=class>Route Classes</span> == | ||
| + | The problem: you want to create a battle arena with 2 levels. The auto-connect calculation must be independent for each level with exception of the passages. '''Block Plaza''' is a good example for this kind of arenas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The solution is to use classes. Every route is part of a class. Or more specific: every end of the route is split in 2 classes: one for incoming connections and one for outgoing connections. So we have 4 classes for each route: | ||
| + | * Class for incoming connections by PREV links. | ||
| + | * Class for outgoing connections by PREV links. | ||
| + | * Class for incoming connections by NEXT links. | ||
| + | * Class for outgoing connections by NEXT links. | ||
| + | The auto-connect function for a PREV link will only search destinations where the incoming PREV class [[#pdclass|matches]] (''not identical'') the outgoing PREV class. And same for the NEXT links. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This concept seems to be difficult, but you don't usually need the full functionality. In fact, the later implemented [[#oneway|one-way]] support is much easier to manage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === <span id=pdclass>Predefined classes</span> === | ||
| + | Classes are automatically defined by the first usage of a class name. Up to 250 classes can be defined, which is much more than needed. There are 3 pre-defined classes with special meanings: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <dl><dt>$OFF</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Class <tt class=code>$off</tt> matches none and disables auto-connect. | ||
| + | </dd><dt>$ANY</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Class <tt class=code>$any</tt> matches all classes other than class <tt class=code>$off</tt>. | ||
| + | </dd><dt>$DEFAULT</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Class <tt class=code>$default</tt> is the default class at the beginning. There is nothing special with it. | ||
| + | </dd></dl> | ||
| + | All standard classes (= all except <tt class=code>$off</tt> and <tt class=code>$any</tt>, but including <tt class=code>$default</tt>) match the same class and class <tt class=code>$any</tt>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Commands, Syntax and Defaults === | ||
| + | There are 4 commands that support the class model: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Syntax: | ||
| + | "$DEF-CLASS" [":"] class_name | ||
| + | "$CLASS" [":"] class_name_prev [class_name_next] | ||
| + | "$AC-PREV" [":"] class_name | ||
| + | "$AC-NEXT" [":"] class_name | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <dl><dt>$DEF-CLASS</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Define a default class for the following <tt class=code>$GROUP</tt> commands. Every new GROUP is initialized by the class of the last <tt class=code>$DEF-CLASS</tt> command. The default group for this command is <tt class=code>$default</tt>. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Example:''' <tt class=code>$DEF-CLASS: upperfloor</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </dd><dt>$CLASS</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Define a class for the current group. If 2 names are given, the first name sets the class for the PREV end, and the second name the class for the NEXT end of the route. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Examples:'''<pre> | ||
| + | $CLASS: upperfloor | ||
| + | $CLASS: upperfloor basefloor | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </dd><dt>$AC-PREV</dt><dd> | ||
| + | Define a class name for an outgoing PREV connection created by auto-connect. If used together with command <tt class=code>$CLASS</tt>, then define <tt class=code>$CLASS</tt> first and then <tt class=code>$AC-PREV</tt>. »AC« means ''auto-connect''. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Example:''' <tt class=code>$AC-PREV: basefloor</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </dd><dt>$AC-NEXT</dt><dd> | ||
| + | <tt class=code>$AC-NEXT</tt> works the same as <tt class=code>$AC-PREV</tt>, | ||
| + | but for the NEXT links. | ||
| + | </dd></dl> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Examples === | ||
| + | The following example shows a part of an arena with two levels. Read the comments inside the code: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #--- Let's start with the basefloor as default class: | ||
| + | $DEF-CLASS basefloor | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Define 2 standard routes (class basefloor): | ||
| + | $ROUTE BR1 | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ROUTE BR2 | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Define 1 dispatch point (class basefloor): | ||
| + | $GROUP BD1 | ||
| + | $SETTINGS 1 0x40 | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Define a passage between floors. The passage is bidirectional, so we use $CLASS. | ||
| + | #--- For one-way passages, $AC-PREV/$AC-NEXT is the better solution. | ||
| + | $GROUP PASS1 | ||
| + | $CLASS basefloor upperfloor | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Now we define the upper float as default class: | ||
| + | $DEF-CLASS upperfloor | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Define 1 dispatch point (class upperfloor): | ||
| + | $GROUP UD1 | ||
| + | $SETTINGS 2 0x80 | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- Define 1 standard route (class upperfloor): | ||
| + | $GROUP UR1 | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== <span id=tune>Fine Tuning</span> == | == <span id=tune>Fine Tuning</span> == | ||
| − | + | Besides [[#class|classes]], there exists more commands that allow fine tuning of the auto-connect algorithm. You can define if a route is [[#dpmodes|standard or a dispatch point]]. There is a way to declare [[#oneway|one-way connections]]. Last but not least, you can set up some routes [[#manual|manually]] and disable the auto-connection. | |
=== <span id=dpmode>Dispatch mode</span> === | === <span id=dpmode>Dispatch mode</span> === | ||
| − | + | Usually, the split between ''standard routes'' and ''dispatch points'' is done by the tools: | |
| + | * Each route with exact one route point and without any PREV link is a dispatch point. | ||
| + | * All other routes are standard routes. | ||
| + | But the user can override this auto detection with the command '''<tt>$SETTINGS</tt>''': | ||
| + | * Syntax: <tt class=code>"$SETTINGS" [":"] setting1 setting2 [ "AUTO" | "ROUTE" | "DISPATCH" ]</tt> | ||
| + | * Default: <tt class=code>$SETTINGS: 0 0 AUTO</tt> | ||
| + | The command starts with the keyword <tt class=code>$SETTINGS</tt> (case insensitive). The following colon is optional. Then, 2 numerical expressions for the 2 settings are expected. The last optional parameter is a keyword (or its unique abbreviation). <tt class=code>AUTO</tt> (the default one, if the parameter is missing) enables the auto detection and the other 2 keywords override it. | ||
| − | + | Example: set the mode of a route with only one route point to ''standard route'': | |
| − | + | $SETTING 0 0 ROUTE | |
=== <span id=oneway>One-way links</span> === | === <span id=oneway>One-way links</span> === | ||
| − | + | Usually, the auto-connect algorithm creates a link from a standard route to the nearest dispatch point, and a second link in the other direction. But sometimes, you only want a one-way connection, for example, to jump down from an upper level to the base level. For this case, command '''<tt>$ONEWAY</tt>''' exists: | |
| + | * Syntax: <tt class=code>"$ONEWAY" [":"] "NONE" | "PREV" | "NEXT" | "BOTH"</tt> | ||
| + | * Default: <tt class=code>$ONEWAY: NONE</tt> | ||
| + | The command starts with the keyword <tt class=code>$ONEWAY</tt> (case insensitive). The following colon is optional. Then, a keyword (or its unique abbreviation) is expected. It declares which end of the route is a one-way connection. The command only has impact for auto-connected standard routes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: set the PREV link to ''one-way'': | ||
| + | $ONEWAY: PREV | ||
| + | |||
| + | One-way links are possible for manual links too. Prefix the destination group name with a »'''>'''«: | ||
| + | $PREV: G1 >G2 G3 | ||
| + | Here, the link to G2 is ''one-way''. | ||
=== <span id=manual>Manual Links</span> === | === <span id=manual>Manual Links</span> === | ||
| − | + | For each single route, standard or dispatch point, it is possible to disable the auto-connect function and to setup the links manually. | |
| + | |||
| + | If at least 1 NEXT link is defined, auto-connect is disabled for the NEXT links. Same for PREV links. If at least 1 PREV link is defined, auto-connect is disabled for the NEXT links. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples: | ||
| + | $GROUP R5, next: DP1 >DP3 | ||
| + | $PREV: DP2 >DP4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is also possible to disable auto-connect if the link list is empty. This is done by using the pre-defined [[#class|class]] <tt class=code>$OFF</tt>: | ||
| + | $AC-PREV $off | ||
| + | $AC-NEXT $off | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Latest revision as of 04:12, 14 April 2021
This tutorial explains the creation of enemy routes in battle arenas using Wiimms SZS Tools. Make sure you have understood the concept of Standard Routes and Dispatch Points!
Introduction
As of v1.60a, Wiimms SZS Tools support an automatic connection of Standard Routes and Dispatch Points. All you need is to set up the routes and points, edit some settings to advise the KMP compiler, and run the compiler. Bash 'n' Dash 'n' Battle is the first arena that used this feature.
There is a second page with full code examples, which are used as reference from this page.
KMP Compiler

When a tool of Wiimms SZS Tools reads a file, the process is always the same: the file is read into memory and analyzed to find out the file format. If the file has an acceptable file format, a scan function is selected and the file data is scanned and translated into the internal data structures, which can hold more data than the files.
In case of KMP (see image on the right), native KMP files and text KMP files are accepted for input. For SZS archives, the file course.kmp is searched for and scanned. Native files are scanned by a binary scanner and text files are translated by the KMP compiler.
Wiimms SZS Tools use a 2-pass compiler to translate KMP text files into the internal data structure. On each pass, the complete text file is scanned. In the first pass, the file is scanned for name definitions. This allows the use of name before it is defined (forward references). Error messages are suppressed. The second pass is used to set up the internal data structure. Error messages about syntax errors or missing names are printed.
The concept of the 2-pass compiler is important for this article, because route links are created by names that are defined later!
The internal data structure allows manipulations of the data in different ways independent of the external file format. Manipulations are for example transformations, but also automatic route connections.
At the end, the data is is stored as binary (commands ENCODE, PATCH), as text (commands DECODE, PATCH, CAT), or dropped (command CHECK).
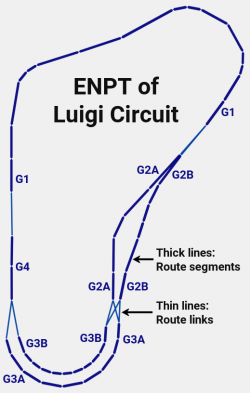
Standard routes only
All 32 original racing tracks, and all custom tracks too, use standard routes. In this case, each end of the routes is linked from 1 to 6 beginnings of other routes. The NEXT links are used for these connections. To get bidirectional links, the PREV links of the destinations are set to the previous routes. The PREV links can be set automatically by analyzing all NEXT links. Wiimm's tools does it, if parameter @AUTO-CONNECT is set to AC$PREV.
Let's look at the group headers of Luigi Circuit. You can find the full de-compiled enemy route definition here.
@AUTO-CONNECT = AC$PREV # == automatic calculation of PREV links # zero based index: 0, prev: 1, next: 4 5 $GROUP G1, next: G2A G2B .... # zero based index: 4, prev: 0, next: 2 3 $GROUP G2A, next: G3A G3B .... # zero based index: 5, prev: 0, next: 2 3 $GROUP G2B, next: G3A G3B
Lines beginning with »#« are comments. Here they show the numerical route index and the links in both directions. For Wiimm's tools, the »$GROUP« tells the compiler to start a new group. The group names are generic, as well as the numbering of group names following the links. In this example, group G1 has 2 successors named G2A and G2B. The PREV links are not defined, because they are calculated automatically.
This concept works for battle arenas too. Nintendo used it for SNES Battle Course 4 (A21). Anyway, using dispatch points is the better concept for battle arenas.
Standard routes and dispatch points
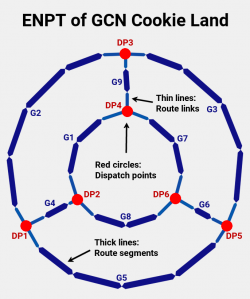
9 of 10 battle arenas made by Nintendo use Dispatch Points. Here we use GCN Cookie Land as an example. You can find the full decompiled enemy route definition here.
The text creator of Wiimm's tools prints the standard routes like this:
# zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 $GROUP G1, next: DP4 $PREV: DP2 .... some points
Each group name begins with »G« like usual. The group name is followed by the NEXT list. This is the same as for racing tracks. In a second line, the PREV links are listed. It is needed because the links are individual and not based on the NEXT links.
A Dispatch Point looks similar, but the names begin with »DP«. This makes differentiation between both route types easier:
# zero based index: 10, prev:, next: 0 3 7 $GROUP DP2, next: G1 G4 G8 $PREV: $SETTINGS: 0 0x80 AUTO .... exact one point
The PREV list is empty. Since there are route setting with values other than zero, an additional $SETTINGS line is printed.
How to create a good ENPT setup
Everything explained above is a large introduction, and here begins the real tutorial with the basics. A later chapter »Fine Tuning« will show, how to handle special cases like route to route links, routes on 2 or more levels and one-way links (e.g. for jumping down).
The base tutorial consists of 4 parts:
- Creating a KMP text file from a binary KMP or from a SZS.
- Editing the text file.
- Verifying the edits.
- Creating the updated KMP or SZS.
Creating a KMP text file
Wiimms SZS Tools are not good to insert routes. There are graphical tools that are definitely better, but this is not really a problem. Insert your routes and your dispatch points too. There is no need to link them, the KMP compiler will do it for you and more.
If you have a binary KMP, just do one of the following:
wkmpt decode course.kmp --battle -od course.kmp.txt wkmpt cat course.kmp --battle >course.kmp.txt
Both commands do the same: load the binary KMP and write a text KMP.
If you KMP is part of a SZS file, you can use the same commands:
wkmpt decode ARENA.szs --battle -od course.kmp.txt wkmpt cat ARENA.szs --battle >course.kmp.txt
It is also possible to extract the whole KMP and re-create the SZS later with the updated KMP:
wszst extract ARENA.szs --battle
In this case, a directory named ARENA.d is created.
Some notes about options:
- Option --battle disables the auto detection of battle arenas and tells the tools that the track file is definitely a battle arena.
- The tools usually don't overwrite existing files. Option --overwrite or short -o disables this security mode.
- Option --dest FILE or -d FILE selects another destination (output) file.
- -od FILE is a short form of -o -d FILE, which is a short form of --overwrite --dest FILE.
- >FILE redirects the output to FILE.
If you are unsure about using the command line, then read this. Windows users can also create batch files like:
@echo off wszst extract ARENA.szs --battle @pause
Edit the ENPT section
The next part is a loop of editing the text file and verifying the results.
To edit the text KMP you need a text editor, but not a document editor like Microsoft Word. A recommendation for Windows users is Notepad++.
Open the KMP text file with the editor. In all the cases above, the filename is course.kmp.txt. Then, scroll to the [ENPT] section. Don't remove or edit any other part, if you don't know what you do. They are needed to re-create the complete KMP file.
Make the following setting (edit the line):
@AUTO-CONNECT = AC$DISPATCH
Below the marker #ENPT# (a comment) you will find the decoded routes. In case of GCN Cookie Land, it looks like here listed.
First, we edit the standard routes. Change this...
# zero based index: 0, prev: 10, next: 12 $GROUP G1, next: DP4 $PREV: DP2
... to this ...
$GROUP G1
...for all standard routes to remove the manual links.
Dispatch points look different. Change this...
# zero based index: 9, prev:, next: 1 3 4 $GROUP DP1, next: G2 G4 G5 $PREV: $SETTINGS: 1 0x40 AUTO
... to this ...
$GROUP DP1 $SETTINGS: 1 0x40
...and remove the PREV and NEXT links. Keep the $SETTINGS line, if you want to keep the settings.
If you have removed all links, you can run the KMP compiler to verify your settings (see next section). The auto-connect function works like this:
- First all routes are divided into 2 sets: standard routes and dispatch points. This is done automatically, but can be controlled by special settings.
- Then, the PREV and NEXT list of all standard routes are analyzed. If an empty list is found, the nearest dispatch point of same class is searched and linked. The class concept is explained in the Fine Tuning part of this tutorial ⇒ ignore it for now.
- Now, all dispatch points are analyzed. If the NEXT list is empty, then all standard routes pointing to the dispatch point are searched. For up to 6 routes, a NEXT link is inserted.
Verify your edits
There are 2 good ways to verify your edits:
- Create a new text KMP from the edited KMP and verify it with an editor, or with the console.
- Create an OBJ file and load it with your favorite 3D Tool.
After verification, you can edit the text KMP again for a next loop.
Create a new text KMP
You can use the same commands described above to create a new text KMP with the edited text as source:
wkmpt decode course.kmp.txt -od verify.txt wkmpt cat course.kmp.txt >verify.txt
If working with a console window, it is possible to pipe the output to a pager and scroll through it. The following command works for Windows and Linux:
wkmpt cat -N course.kmp.txt | more
Linux users (Cygwin users too) can use the more powerful tool less instead of the classic more:
wkmpt cat course.kmp.txt |& less +/'^!|#ENP'
The option +/'^!|#ENP' enables searching for errors and data of sections ENPH and ENPT. Type »n« to jump to the next matching line.
Section ENPH gives an overview about all routes and its links. Section ENPT shows the routes with the new calculated connections.
Create an OBJ file
A second method for verification is to export the data to a Wavefront OBJ file and to open it with any 3D Tool.
wkmpt draw course.kmp.txt --draw enpt,white -od path/to/a.obj
With these options, only the enemy routes are drawn. A white ground is added for an optimal view from the top. The example image from above is made by this.
Alternatively, you can visualize the KCL:
wkmpt draw course.kmp.txt --draw enpt,kcl -od path/to/a.obj
Create a new course.kmp or TRACK.szs
To create a binary KMP, use the command:
wkmpt encode course.kmp.txt -od new-course.kmp
If you have extracted a complete SZS file, use the following command to create a new one:
wszst create ARENA.d -od new.szs
If you modify the file course.kmp.txt, a new course.kmp is automatically created.
Route Classes
The problem: you want to create a battle arena with 2 levels. The auto-connect calculation must be independent for each level with exception of the passages. Block Plaza is a good example for this kind of arenas.
The solution is to use classes. Every route is part of a class. Or more specific: every end of the route is split in 2 classes: one for incoming connections and one for outgoing connections. So we have 4 classes for each route:
- Class for incoming connections by PREV links.
- Class for outgoing connections by PREV links.
- Class for incoming connections by NEXT links.
- Class for outgoing connections by NEXT links.
The auto-connect function for a PREV link will only search destinations where the incoming PREV class matches (not identical) the outgoing PREV class. And same for the NEXT links.
This concept seems to be difficult, but you don't usually need the full functionality. In fact, the later implemented one-way support is much easier to manage.
Predefined classes
Classes are automatically defined by the first usage of a class name. Up to 250 classes can be defined, which is much more than needed. There are 3 pre-defined classes with special meanings:
- $OFF
- Class $off matches none and disables auto-connect.
- $ANY
- Class $any matches all classes other than class $off.
- $DEFAULT
- Class $default is the default class at the beginning. There is nothing special with it.
All standard classes (= all except $off and $any, but including $default) match the same class and class $any.
Commands, Syntax and Defaults
There are 4 commands that support the class model:
Syntax: "$DEF-CLASS" [":"] class_name "$CLASS" [":"] class_name_prev [class_name_next] "$AC-PREV" [":"] class_name "$AC-NEXT" [":"] class_name
- $DEF-CLASS
-
Define a default class for the following $GROUP commands. Every new GROUP is initialized by the class of the last $DEF-CLASS command. The default group for this command is $default.
Example: $DEF-CLASS: upperfloor - $CLASS
-
Define a class for the current group. If 2 names are given, the first name sets the class for the PREV end, and the second name the class for the NEXT end of the route.
Examples:$CLASS: upperfloor $CLASS: upperfloor basefloor
- $AC-PREV
-
Define a class name for an outgoing PREV connection created by auto-connect. If used together with command $CLASS, then define $CLASS first and then $AC-PREV. »AC« means auto-connect.
Example: $AC-PREV: basefloor - $AC-NEXT
- $AC-NEXT works the same as $AC-PREV, but for the NEXT links.
Examples
The following example shows a part of an arena with two levels. Read the comments inside the code:
#--- Let's start with the basefloor as default class: $DEF-CLASS basefloor #--- Define 2 standard routes (class basefloor): $ROUTE BR1 .... $ROUTE BR2 .... #--- Define 1 dispatch point (class basefloor): $GROUP BD1 $SETTINGS 1 0x40 .... #--- Define a passage between floors. The passage is bidirectional, so we use $CLASS. #--- For one-way passages, $AC-PREV/$AC-NEXT is the better solution. $GROUP PASS1 $CLASS basefloor upperfloor .... #--- Now we define the upper float as default class: $DEF-CLASS upperfloor .... #--- Define 1 dispatch point (class upperfloor): $GROUP UD1 $SETTINGS 2 0x80 .... #--- Define 1 standard route (class upperfloor): $GROUP UR1 ....
Fine Tuning
Besides classes, there exists more commands that allow fine tuning of the auto-connect algorithm. You can define if a route is standard or a dispatch point. There is a way to declare one-way connections. Last but not least, you can set up some routes manually and disable the auto-connection.
Dispatch mode
Usually, the split between standard routes and dispatch points is done by the tools:
- Each route with exact one route point and without any PREV link is a dispatch point.
- All other routes are standard routes.
But the user can override this auto detection with the command $SETTINGS:
- Syntax: "$SETTINGS" [":"] setting1 setting2 [ "AUTO" | "ROUTE" | "DISPATCH" ]
- Default: $SETTINGS: 0 0 AUTO
The command starts with the keyword $SETTINGS (case insensitive). The following colon is optional. Then, 2 numerical expressions for the 2 settings are expected. The last optional parameter is a keyword (or its unique abbreviation). AUTO (the default one, if the parameter is missing) enables the auto detection and the other 2 keywords override it.
Example: set the mode of a route with only one route point to standard route:
$SETTING 0 0 ROUTE
One-way links
Usually, the auto-connect algorithm creates a link from a standard route to the nearest dispatch point, and a second link in the other direction. But sometimes, you only want a one-way connection, for example, to jump down from an upper level to the base level. For this case, command $ONEWAY exists:
- Syntax: "$ONEWAY" [":"] "NONE" | "PREV" | "NEXT" | "BOTH"
- Default: $ONEWAY: NONE
The command starts with the keyword $ONEWAY (case insensitive). The following colon is optional. Then, a keyword (or its unique abbreviation) is expected. It declares which end of the route is a one-way connection. The command only has impact for auto-connected standard routes.
Example: set the PREV link to one-way:
$ONEWAY: PREV
One-way links are possible for manual links too. Prefix the destination group name with a »>«:
$PREV: G1 >G2 G3
Here, the link to G2 is one-way.
Manual Links
For each single route, standard or dispatch point, it is possible to disable the auto-connect function and to setup the links manually.
If at least 1 NEXT link is defined, auto-connect is disabled for the NEXT links. Same for PREV links. If at least 1 PREV link is defined, auto-connect is disabled for the NEXT links.
Examples:
$GROUP R5, next: DP1 >DP3 $PREV: DP2 >DP4
It is also possible to disable auto-connect if the link list is empty. This is done by using the pre-defined class $OFF:
$AC-PREV $off $AC-NEXT $off
Links
Main Tutorials
Introduction –
Textures –
Scale –
Modeling ⇒ Using Blender –
BRRES: CTools
BRRES: BrawlBox –
BRRES: RiiStudio –
Minimap –
Solidity –
KCL: Wiimms Tools –
KMP Editing
Object Editing –
Cameras –
Cannons –
Post-effects –
Videos
Battle Arenas
Battle Arenas –
Enemy routes in battle arenas ⇒ Using Wiimm's Tools –
Coins
Misc. Tutorials
Getting Files –
BrawlBox Tricks –
Animations –
Shadows –
Mipmaps
Custom Effects –
Moving Terrain –
Music –
Ports –
Paint Remakes –
Tutorial Archive
Extended presence flags: Track Tutorial –
LE-CODE Track FAQ
Testing and Reviewing
Testing a Track –
Visual Review –
Track Transformation –
Fixing Errors
Software
3D Tools –
BrawlBox –
CTools Pack –
KMP3D –
KMP Cloud –
KMP Modifier
Lorenzi's KMP Editor –
MagicY –
Material Tool –
Post-Effect Editor –
Wiimms SZS Tools –
Wiimm's Tool Manager
Other
KMP Objects –
Custom Objects –
Model Database –
Tutorial Archive